
Teaching Physics with the Physics Suite
Edward F. Redish Home | Action Research Kit| Sample Problems | Resources | Product Information
Problems Sorted by Type | Problems Sorted by Subject | Problems Sorted by Chapter in UP
 |
Teaching Physics with the Physics Suite
Edward F. Redish Home | Action Research Kit| Sample Problems | Resources | Product Information |
Problems Sorted by Type | Problems Sorted by Subject | Problems Sorted by Chapter in UP |
An ammeter is an instrument that shows how much current passes through it. It is designed to have a small resistance. The following problems show why.
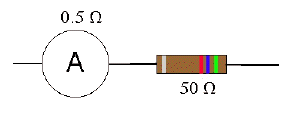
A. Suppose an ammeter having a resistance of 0.5 Ω is connected in parallel across a resistor of 50.0 Ω as shown in the figure at the right.
|
 |
B. Suppose instead the ammeter were in series with the resistor as shown in the figure at the right.
|
 |
A voltmeter is also a device that shows the voltage difference across its terminals, but it has a very large resistance. The next two problems show why.
C. Suppose a voltmeter having a resistance of 1500 Ω were in series with a resistor of 50.0 Ω as shown in the figure at the right.
|
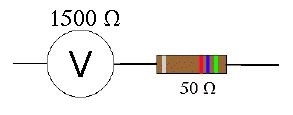 |
D. Suppose instead, the voltmeter were in parallel with the resistor as shown in the figure at the right.
|
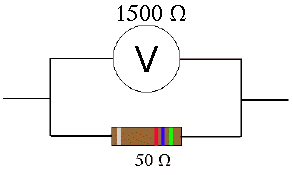 |
E. So if you were to hook up an ammeter or a voltmeter to measure the current through a resistance or the voltage drop across a resistance respectively, how would you connect it?
Page last modified May 1, 2009: E36