


Next: Temperature
Up: Homework Problems for PHYS262,
Previous: Fluids
- 3-1
- A travelling wave on a string is described by
where 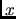 and
and 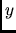 are
in centimetres and
are
in centimetres and 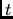 is in seconds (a) for
is in seconds (a) for 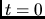 , plot
, plot 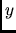 as a
function of
as a
function of 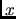 for
for
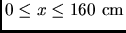 . (b) Repeat (a) for
. (b) Repeat (a) for 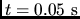 and
and
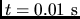 . (c) From your graphs, what is
the wave speed, and in which direction (
. (c) From your graphs, what is
the wave speed, and in which direction (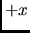 or
or 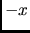 ) is the wave travelling?
) is the wave travelling?
- 3-2
- What is the fastest transverse wave that can be sent along a steel
wire? Allowing for a reasonable safety factor, the maximum tensile
stress to which stress to which steel wires should be subject is
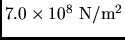 .
The density of steel is
.
The density of steel is
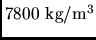 .
Show that your answer does not depend on
the diameter of the wire.
.
Show that your answer does not depend on
the diameter of the wire.
- 3-3
- A series of pulses, each of amplitude 0.150 m, are sent
down a string that is attached to a post at one end. The pulses are
reflected at the post and travel back along the string without loss of
amplitude. What is the displacement at a point on the string where
two pulses are crossing (a) if the string is rigidly attached to the
post? (b) If the end at which reflection occurs is free to slide up
and down?
- 3-4
- A transverse sinusoidal wave on a string has a period
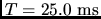 and travels in the negative
and travels in the negative 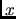 direction with a speed of
direction with a speed of 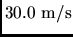 . At
. At
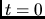 , a particle on a string at
, a particle on a string at 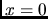 has a displacement of
has a displacement of 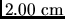 and
travels downward with a speed of
and
travels downward with a speed of 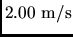 . (a) What is the amplitude of
the wave? (b) What is the initial phase angle? (c) What is the
maximum transverse speed of the string? (d) Write the wave function
for the wave.
. (a) What is the amplitude of
the wave? (b) What is the initial phase angle? (c) What is the
maximum transverse speed of the string? (d) Write the wave function
for the wave.
- 3-5
- An acoustic microscope can form a remarkably detailed
image of microelectronic circuits such as transistors. The sound waves
have a frequency of
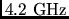 . The speed of such waves in the
liquid helium in which the specimen is immersed is
. The speed of such waves in the
liquid helium in which the specimen is immersed is 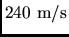 . (a)
What is the wavelength of these ultra-high-frequency acoustic waves?
(b) You wish to take images of circuits of conductors that are
approximately
. (a)
What is the wavelength of these ultra-high-frequency acoustic waves?
(b) You wish to take images of circuits of conductors that are
approximately 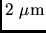 wide. To how many wavelengths does this
correspond?
wide. To how many wavelengths does this
correspond?
- 3-6
- A sinusoidal sound wave is described by the displacement
(a) find the amplitude, wavelength and speed of this wave. (b)
Determine the instantaneous displacement of the molecules at the
position
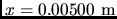 at
at
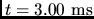 . (c) Determine the
maximum speed of the molecule's oscillator motion.
. (c) Determine the
maximum speed of the molecule's oscillator motion.
- 3-7
- Two identical travelling waves, moving in the same direction, are out
of phase by
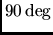 . What is the amplitude of the combined wave in terms
of the common amplitude
. What is the amplitude of the combined wave in terms
of the common amplitude 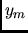 of the two combining waves?
of the two combining waves?
- 3-8
- Two loudspeakers,
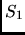 and
and 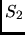 , are 7.0 m apart. Each
emits a sound frequency of 200 Hz, uniformly in all directions.
, are 7.0 m apart. Each
emits a sound frequency of 200 Hz, uniformly in all directions. 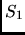 has an acoustic output of
has an acoustic output of
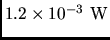 and
and 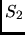 one of
one of
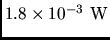 .
. 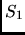 and
and 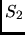 vibrate in phase. Consider a point
vibrate in phase. Consider a point 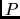 that is 4.0 m from
that is 4.0 m from 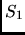 and 3.0
m from
and 3.0
m from 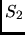 . (a) How are the phases of the two waves arriving at
. (a) How are the phases of the two waves arriving at 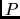 related? (b) What is the intensity of sound at
related? (b) What is the intensity of sound at 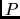 with both
with both 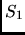 and
and
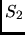 on? (c) What is the intensity of sound at
on? (c) What is the intensity of sound at 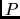 if
if 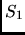 is turned
off (
is turned
off (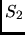 on)? (d) What is the intensity of sound at
on)? (d) What is the intensity of sound at 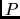 if
if 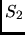 is turned
off (
is turned
off (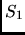 on)?
on)?
- 3-9
- A 15-cm violin string, fixed at both ends, is vibrating in
its
 mode. The speed of waves in this wire is 250 m/s,
and the speed of sound in air is 348 m/s. What
are (a) the frequency and (b) the wavelength of the emitted sound wave?
mode. The speed of waves in this wire is 250 m/s,
and the speed of sound in air is 348 m/s. What
are (a) the frequency and (b) the wavelength of the emitted sound wave?
- 3-10
- A 75 cm string is stretched between fixed supports. It is
observed to have resonant frequencies of 420 and 315 Hz, and no other
resonant frequencies between the two. (a) What is the lowest resonant
frequency for this string? (b) What is the wave speed for this string?
- 3-11
- A tuning fork of unknown frequency makes 3 beats per
second with a standard fork of frequency 384 Hz. The beat frequency
decreases when a small piece of wax is put on a prong of the first
fork. What is the frequency of this fork?
- 3-12
- A string 2.7 m long has a mass of 260 g. The tension in
the string is 36 N. What must be the frequency of travelling waves of
amplitude 7.7 mm in order that the average transmitted power be 85 W?
- 3-13
- A vacuum cleaner has a measured sound level of 70 dB. (a)
What is the intensity of this sound in watts per square meter? (b)
What is the pressure amplitude of this sound?
- 3-14
- A whistle used to call a dog has a frequency of 30 kHz.
The dog, however, ignores it. The owner of the dog, who cannot hear
sounds above 20 kHz, wants to use the Doppler effect to make certain
that the whistle is working. She asks a friend to blow the whistle
from a moving car, while the owner remains stationary and listens. (a)
How fast must the car move and in what direction? Is the experiment
practical? (b) Repeat for a whistle frequency of 22 kHz instead of 30
kHz.
- 3-15
- The ``red shift'' of radiation from a distant galaxy
consists of the light
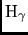 , known to have a wavelength of 434 nm when
observed in the laboratory, appearing to have a wavelength of 462
nm. (a) What is the speed of the galaxy in the line of sight relative
to the earth? (b) Is it approaching or receding?
, known to have a wavelength of 434 nm when
observed in the laboratory, appearing to have a wavelength of 462
nm. (a) What is the speed of the galaxy in the line of sight relative
to the earth? (b) Is it approaching or receding?



Next: Temperature
Up: Homework Problems for PHYS262,
Previous: Fluids
HJK
2001-07-22